
Psychometer
The psychrometer measures so called relative humidity - not the volume of water vapour in the air in absolute units, but the potential capacity of air to 'accommodate' water vapour at a given temperature. Relative humidit "w" (percentage share) can be calculated with the application of the following formula:
in which e is the compressibility of vapour at a given temperature and pressure E is the compressibility of saturated vapour under the same conditions.
JW Player goes here
|
Sprung's equation can be applied to calculate "e" value.
E1 is compressibility of saturated vapour at the temperature shown by the moistened (T1) thermometer, p, stands for pressure (in hPa), and C is psychometric coefficient equal 0.5 for water and 0.43 for ice.
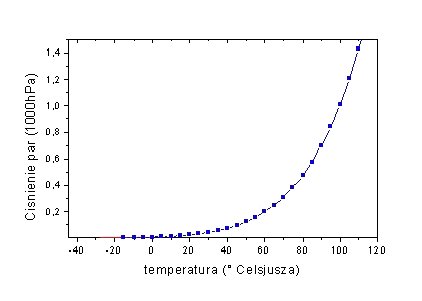
Since the relation for E1 p is quite complicated and it is non-linear, as can be seen on the graph, the assessment of the volume of humidity is arrived upon reading the temperature on both thermometers and interpreting this information with the special tables.
Thus, at the temperatures of 200 C and 100 C as shown by a regular and moistened
thermometer respectively the relative humidity is 24%, at 300 C and 200 C the relative humidity is 39%. Generally, the smaller the difference between the temperatures shown by two thermometer, the higher the humidity. And vice versa, the bigger the difference, the drier the air. The above relations are non-linear, because of non-linear relationship between compressibility of saturated vapour and temperature.