Warm Coffee

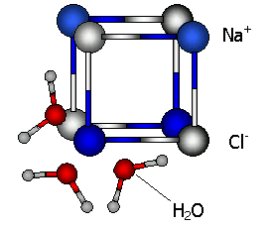
During the process of dissolving, water molecules, possessing a high dipole moment, interact with cations and anions (positive or negative ions, see Volta's tongue) of the dissolving material. The oxygen part of a water molecule attaches to positive ions and the hydrogen part sticks to negative ions and detach them form the solid. Mixing brings new water molecules to the solid and accelerates the salvation process (is more rapid). Let us consider the dissolving process in two steps.
First, as a result of dissolving cations and anion, free spaces are filled by free atoms or molecules. The value of the energy associated with such a process (in chemistry it is better to say "enthalpy" instead of energy) is equal to the enthalpy associated with the formation of the solid from gas. For calcium chloride the calculation gives
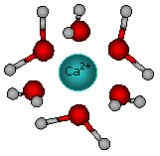
Next, ions get inside the liquid - water molecules concentrate around ions. As the interaction between ions and water (or other liquid) molecules is attractive, the enthalpy of this process is always negative (the energy is gained
For this process DHhyd = - 2337 kJ.
The total change of enthalpy is the sum of these two processes. In the case of calcium chloride, this sum equals DH = -77 kJ. The negative sign means that heat is formed during dissolving - the coffee mug becomes warm. Other substances require the energy from outside to be dissolved - the coffee gets cold.