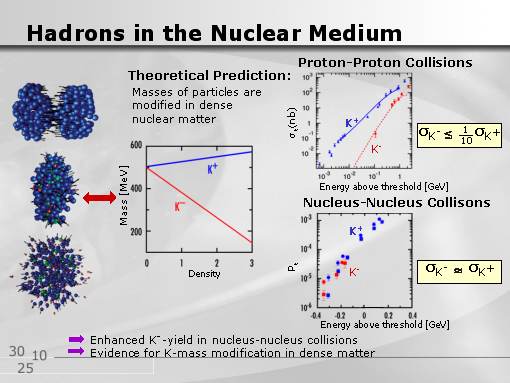
In spite of the fact that K
+ (with quark content
us) and K
- (
us) mesons seems to be
completely "symmetrical", their behaviour in presence of other quarks is
not the same. Duringa a collision of proton (
udd) with another proton
to create K
+ kaon, there is necessary creation of one
s
antiquark, and for creation of K
- kaon, there is needed creation
of
s quark and simoultaneously change of u w antykwark
u.
From this reason during proton - proton collisions (plot on right top) probability
of creation K
- kaon, especially with small energy range of collisions,
is decisively lower than K
+ kaon creation probability.
Theoretical model (plot on left) predicts, that K
- meson mass
decreases with
increase of density of sorrounding
it nuclear matter, but for K
+ meson mass increase (from about 493
MeV, which is value for free mesons). As far as in free protons collisions
probability of creation of K
+ i K
- mesons is not the
same, for nuclei collisions (such experiments are performed in
Darmstadt) mass change effect causes, that probability
are the same (plot on right low).