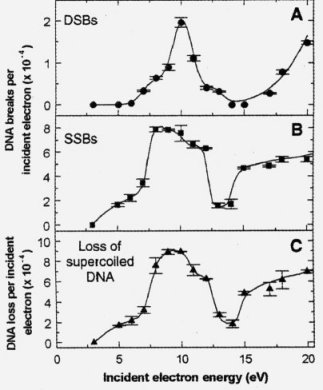
Fig. 1 DNA structure damages caused by low-energy electrons.
Cosmic radiation, both primary (protons with energy range from 10-7 to 10-20 eV, positrons, electrons, gamma radiation) and secondary (mainly mions and electrons created in their decay) causes biological damages of different kinds, among others in the DNA structure (mutations, genotype recombinations, denaturation of DNA). However it seems, that these damages are not caused by the radiation itself, but mainly by electrons created in living cells in ionization events, for example particles of water. Energy of such electrons is in range from 1 to 20 eV, what theoretically is not sufficient to ionize complex molecules (for example the ionization threshold for ethyl alcohol is equal to 10.5 eV). Until recent time it was not sure, if such low energy electrons can cause genetic damages of DNA, like SSB (Single Strand Break) - breake of one DNA helix or DSB (Double Strand Break) - breaking both strips of the helix.Electron attachment in DNA
1. Very low energy electrons cause DNA damages (both SSB and DSB) even at energies below ionization threshold of DNA (from 7.5 up to 10 eV).

Fig. 1 DNA structure damages caused by low-energy electrons.
A similar damage mechanism was observed in the case of thin layers containing water, thymine and desoxyribose analog (Fig. 2).RH*- = R + H-.
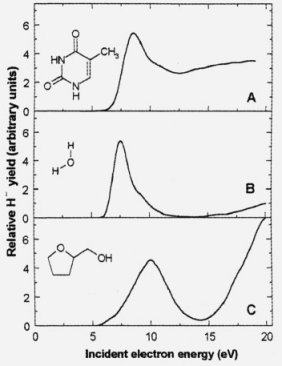
Fig. 2 Electron-induced damages in molecules in a condensed film phase (A - thymine, B - water, C - tetrahydrofuryl alcohol).
