|
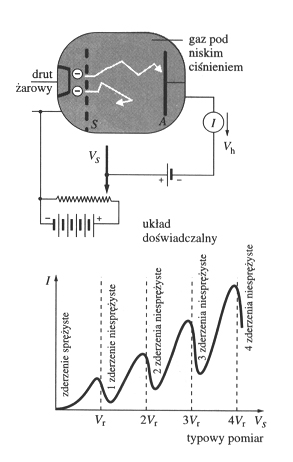
Schematics and result of Franck-Hertz experimentElectrons are emitted from cathode. At grid S is given adjusted voltage (from zero to teenth V) accelerating electrons. Between grid and anode A, small, constant stopping voltage, which don'a allow to too slow electrons to reach anode. Without collisions, with increase of grid voltage, electron current should grow (of in saturation conditions it should be constant). In triode filled with the mercury vapour this increase is not monotonic, and curve falls down when electrons have sufficient energy to excite mercury atoms to higher electronic state. It means: mercury atoms are not only emitting energy as a (light) quanta, but also are absorbing energy (from free electrons) as a quanta. This pictrure is from: |