J.-B.-J. Fourier (1768-1830).
Napoleon made in Egypt two invaluable discoveries: the basalt plate, known as „la Rosette" and the professor of analysis of Polytechnic Čcole Jean-Baptist-Joseph Fourier.
The first, containing one of the decrees of Ptolemeus V(196 D.C.) registered in hieroglyphes, demotic and Greek allowed in 1822 J.F. Champollion to decode the Egyptian writing. |
La Pierre de Rosette, British Museum |
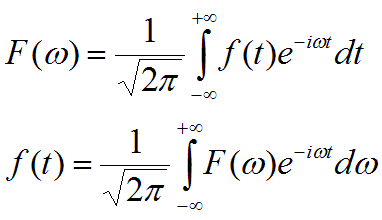
Transformation of Fourier and reverse transformation.
The analysis of Fourier makes it possible to decode the components of an unspecified periodic function.
Transformation of Fourier "seeks" if in the periodic function (as a vibration) are specific frequencies: the periodic function of period 2π is developed in series:
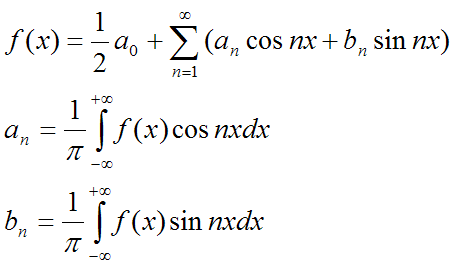
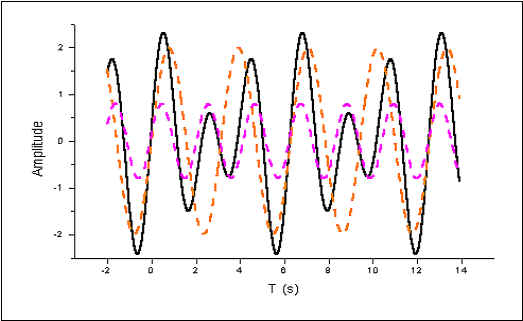
The black curve has two components: sin2x and sin(3x+0.2); it is superimposed with the pink sinusoid the two periods, with the orange sinusoid the three periods.
An oscillation which is propagated in space (e.g. along x axis), becomes "a wave".
ζ (x,t)=A sin (ωt – kx), where the period is T=2π/ω and the wavelength is λ=2π/k.
The sound is a simple example of wave. The human ear is able to recognize the sound of a particular individual musical instrument in the symphony in full orchestratration. Ear makes it by that an analysis of Fourier.
There is 100 years since the analysis of Fourier was done via complicated mechanical devices: masses oscillating or sphere vacuums, for the sound. Today one analyzes the sound with a simple computer and the virtual oscilloscope (http://polly.phys.msu.su/~zeld/oscill.html)
 |
|
|
Virtual oscilloscope |
Sound analyzer of König (Charles University, Prague) |
Harmonic analyzer of de Sir. W. Thomson |
These small African artisanal animals make the same operation as the complicated analyzer of Sir Thomson and H. Helmholtz: they raise the vibrations, each one at its particular own frequency!
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
The oscillating towers are in front of the Faculty of Chemistry of the University of Berlin